The Ebola virus disease (EVD) is a fatal condition that has caused thousands of deaths across the globe. It affects people and non-human primates, such as chimpanzees, monkeys and gorillas.
Learn more about the deadly disease with these surprising facts about Ebola.
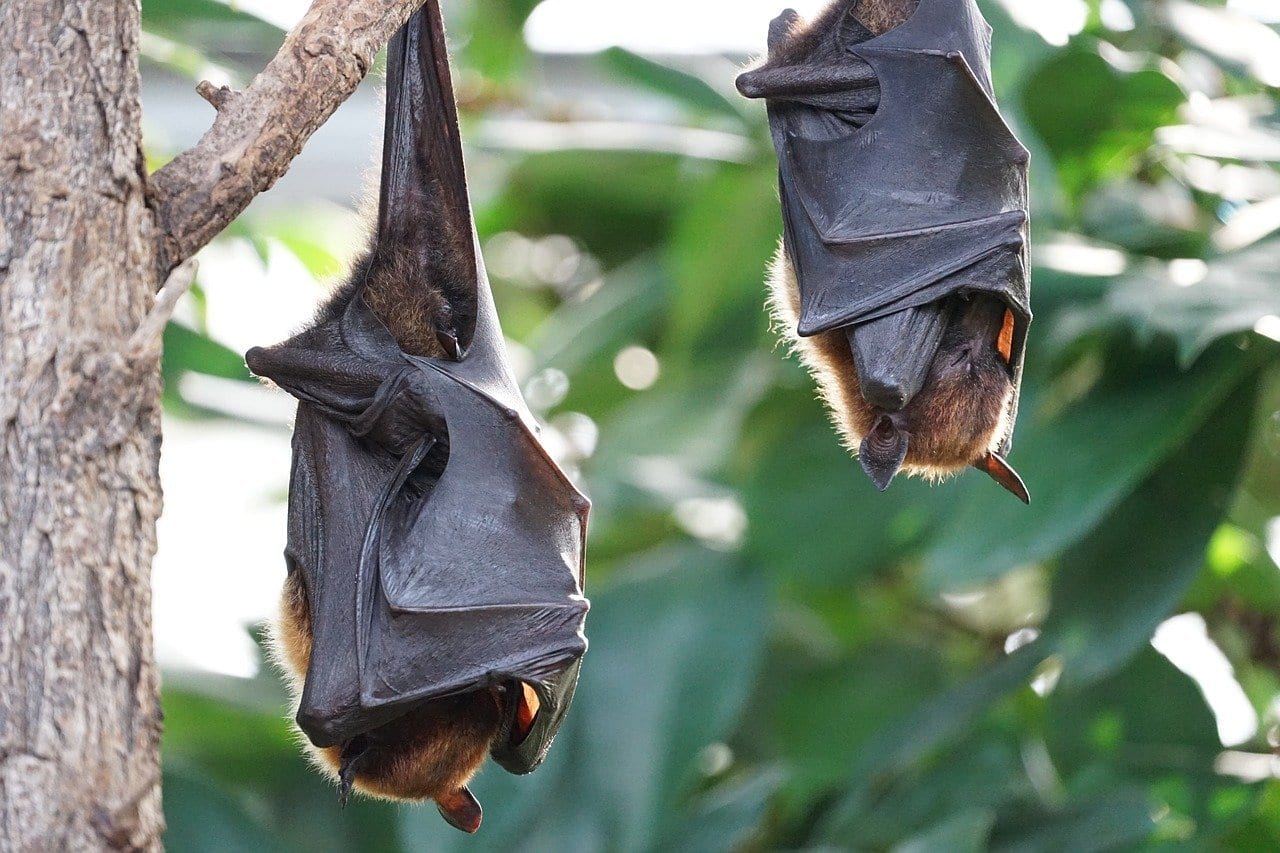
1. Are bats to blame?
Scientists have yet to confirm where the virus comes from, but they suspect that it’s animal-borne. Bats and non-human primates are the most likely source.
2. Ebola is older than you think.
The Ebola virus was first discovered in 1976 but it has existed for over 10,000 years.
3. Rest easy – you probably won’t get it.
EVD isn’t as contagious as many people believe. The virus only survives about 30 seconds outside of a bodily fluid, so infection rates are lower than other diseases.

4. There’s no cure for Ebola.
To date, there is still no approved drug for treating EVD, although several vaccines are already undergoing clinical trials.
5. Thousands have died from deadly Ebola strains.
The West African Ebola virus that lasted from 2013 to 2016 has caused over 11,300 fatalities.
6. Outbreaks have come and gone.
The West African Ebola virus outbreak ended on 13 January, 2016. The World Health Organization declared Liberia, the last country affected, to be Ebola-free then.
7. You’re not ‘clean’ for some time.
EVD is transmitted through the body fluids of a person who has contracted the virus. The virus can still survive in the semen for up to 9 months even when the patient has recovered.
8. Ebola doesn’t die with the host.
The bodily fluids of someone who died from EVD can still transmit the virus to living people. Yes, you can catch Ebola from a dead body.
9. It’s not always easy to spot.
The early symptoms of EVD are similar to other illnesses, making it difficult to diagnose.
10. Ebola’s evolved many times.
There are five species of Ebola virus, with the Zaire strain being the most fatal. It caused the largest outbreak in history, which is the one in West Africa.
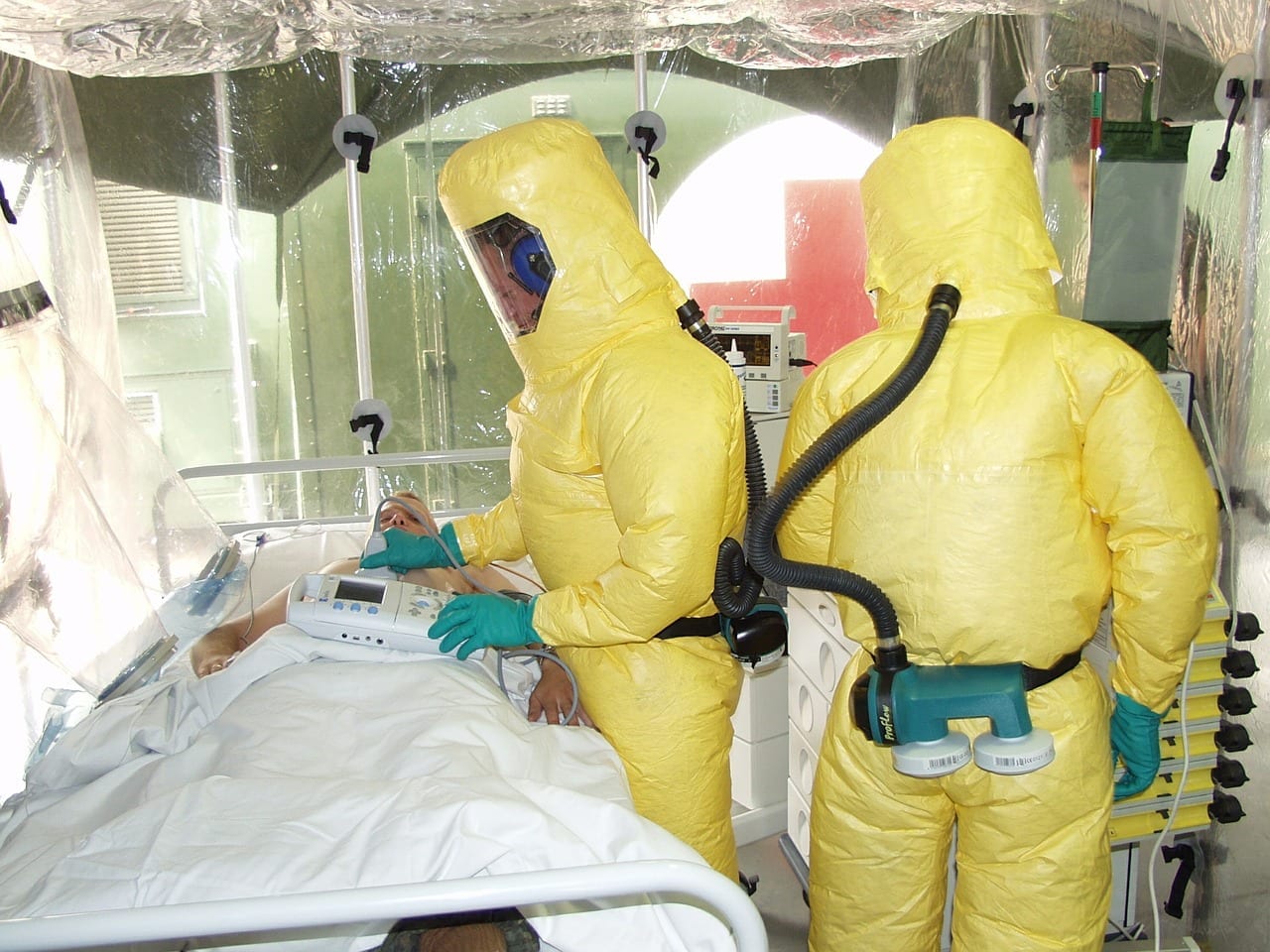
FAQs about Ebola
Can you survive Ebola?
Yes - it’s entirely possible to survive Ebola, though you’ll need to be treated carefully. It’s a disease that can be fought easily with strong immunity.
How long do Ebola antibodies last?
Typically, a survivor of Ebola can expect antibodies to persist for up to ten years after recovery.
What’s Ebola’s mortality rate?
Ebola’s mortality rate is 50%, though this has risen to 90% - and as low as 25% - in previous outbreaks.
Do you know any interesting facts about the Ebola virus? Share them in the comments below!